

Views: 222 Author: Ella Publish Time: 2025-05-23 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● The Importance of Sharpening Japanese Knives
● Top Japanese Knife Sharpener Manufacturers
>> Kyocera
>> King
>> Takeuchi
>> Asahi Industry Co., Ltd. (TOGISHI)
>> Minosharp
>> Miyabi (Zwilling J.A. Henckels Group)
● Types of Japanese Knife Sharpeners
>> Whetstones (Sharpening Stones)
>> Honing Rods
● Traditional Japanese Sharpening Techniques
● Modern Innovations in Japanese Knife Sharpeners
● Choosing the Right Japanese Knife Sharpener
● Professional Sharpening Services in Japan and Abroad
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What types of knives can Japanese sharpeners handle?
>> 2. How often should I sharpen my Japanese knife?
>> 3. Can I sharpen my Japanese knife myself?
>> 4. What is the difference between honing and sharpening?
>> 5. Are electric sharpeners suitable for Japanese knives?
Japan's reputation for exceptional kitchen knives is well established, but equally important is the art of sharpening these blades to maintain their legendary performance. Japanese knife sharpeners are crafted with the same dedication to precision, quality, and tradition as the knives themselves. This article offers an in-depth look at the top knife sharpener manufacturers in Japan, the types of sharpeners available, traditional and modern sharpening techniques, and how to choose the right sharpener for your needs.
Japanese knives are often made from harder steel than Western knives, resulting in thinner, sharper blades that require careful maintenance. The sharpening process not only restores the cutting edge but also preserves the blade's structural integrity and longevity. Using the right sharpener and technique is critical to avoid damaging these finely crafted tools.
Shimomura Kogyo is celebrated for its innovative handheld sharpeners that combine diamond and ceramic abrasive surfaces. Their dual-stage sharpener allows aggressive sharpening with diamond wheels and fine polishing with ceramic wheels, all in a compact, ergonomic design that does not require soaking in water.
Kyocera specializes in ceramic knife sharpeners, ideal for maintaining ceramic and steel blades. Their diamond wheel sharpeners offer efficient sharpening with safety features such as non-slip handles and blade guides, suitable for a variety of blade materials including titanium.
King is a traditional leader in whetstones, producing a range of synthetic sharpening stones with various grits. Their stones are favored for their balance of quality and affordability, perfect for both beginners and professionals who prefer the authentic whetstone sharpening experience.
Takeuchi's patented kitchen knife sharpeners use diamond wheels and require minimal effort, employing a unique edible grease to restore sharpness. Their products are designed for both professional chefs and home users, capable of sharpening a wide range of kitchen knives.
Asahi Industry's TOGISHI sharpener mimics traditional whetstone sharpening but uses diamond-coated stones that require no water. It sharpens knives quickly and effectively, adjustable for different blade thicknesses, and is suitable for stainless steel, iron, and titanium blades.
Minosharp offers user-friendly handheld sharpeners with water reservoirs to reduce heat from friction. Their color-coded wheels indicate stages of sharpening from rough to super-fine, making them versatile for almost all knife types, including Japanese blades.
Miyabi combines Japanese craftsmanship with German engineering, producing handheld sharpeners with diamond and ceramic wheels. Their ergonomic designs ensure comfortable use and deliver sharp, polished edges comparable to electric sharpeners.
Zwilling's sharpeners feature multiple slots for Asian and Western knives, with ergonomic handles and rubberized bases for stability. Their four-stage system allows users to choose the appropriate sharpening level, ensuring precision and safety.

Whetstones are the traditional and most respected sharpening tools in Japan. They come in a variety of grits:
- Coarse (400-1000 grit): For repairing chips and reshaping edges.
- Medium (1000-3000 grit): For sharpening dull knives.
- Fine (3000-6000 grit): For refining edges.
- Ultra-fine (6000-10000+ grit): For polishing to a mirror finish.
Before use, whetstones must be soaked in water to activate their abrasive properties and prevent overheating the blade. Maintaining a consistent sharpening angle, typically around 15 degrees, is vital to achieve a sharp and durable edge. Traditional techniques involve specific motions such as back-and-forth or sweeping strokes, requiring patience and practice to master.
Handheld sharpeners are portable and convenient for quick touch-ups. They often combine diamond-coated wheels for coarse sharpening and ceramic wheels for fine honing. These sharpeners are easy to use and do not require soaking, making them popular for home cooks.
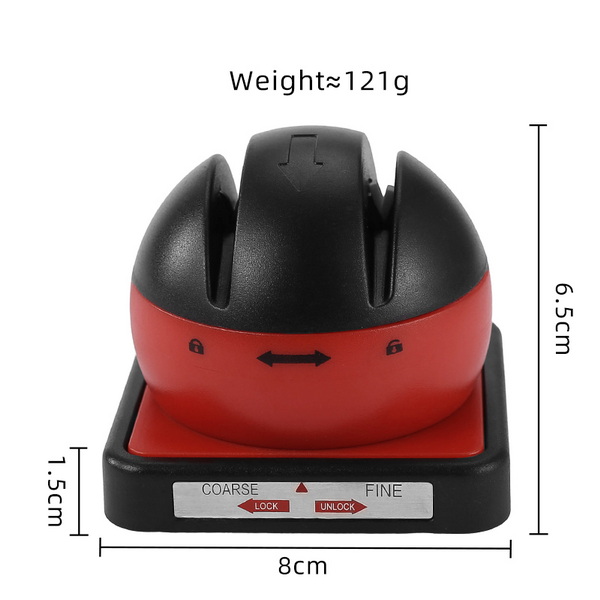
Electric sharpeners use motorized grinding wheels or belts to sharpen knives quickly. They often have multiple stages and angle guides to accommodate different knife types. While convenient, they can remove more metal than manual methods and should be used carefully, especially on delicate Japanese blades.
Honing rods do not sharpen by removing metal but realign the blade's edge to maintain sharpness between sharpenings. They are essential tools for prolonging the life of a sharp knife.
The cornerstone of Japanese knife sharpening is the whetstone method, perfected over centuries. The process includes:
1. Selecting the Right Stone: Depending on blade condition and desired sharpness, choosing the correct grit is essential.
2. Soaking the Stone: Most whetstones require soaking in water before use.
3. Maintaining the Correct Angle: Consistency in angle ensures a sharp, durable edge.
4. Sharpening Motion: Techniques such as the “back and forth” or “sweeping” motion help create a razor-sharp edge.
5. Polishing: Using finer grit stones to polish the blade to a mirror finish.
Mastering this technique demands patience and muscle memory, but the outcome is a blade that cuts with precision and ease.
While traditional whetstones remain popular, modern Japanese manufacturers have introduced innovative products that blend tradition with technology:
- Diamond-coated wheels provide faster sharpening and longer-lasting abrasives.
- Dual-stage handheld sharpeners combine coarse and fine sharpening in one device.
- Water reservoirs in handheld sharpeners reduce heat and friction.
- Ergonomic designs improve safety and comfort during sharpening.
These innovations make sharpening more accessible without compromising the quality of the edge.
When selecting a sharpener, consider:
- Knife type: Some sharpeners are better suited for high-carbon steel, others for ceramic or titanium.
- Sharpening method: Manual whetstones offer control but require skill; handheld sharpeners are convenient; electric sharpeners are fast but may be aggressive.
- Budget: Whetstones and professional services may cost more upfront but offer superior results.
- Skill level: Beginners may prefer handheld or electric sharpeners, while professionals often favor whetstones.
Popular brands like King, Kyocera, Minosharp, and Miyabi offer options for all skill levels and budgets.
For those who prefer expert care, professional sharpening services are available both in Japan and internationally. These services use traditional hand sharpening techniques to restore knives to their maximum potential. They can handle:
- Edge sharpening and honing
- Chip and tip repairs
- Rust removal
- Reprofiling and thinning
Turnaround times vary but typically range from same-day service for minor touch-ups to one or two weeks for extensive repairs.
Japanese knife sharpeners represent a perfect blend of tradition and innovation, designed to preserve the sharpness and longevity of some of the world's finest knives. Whether you choose traditional whetstones, modern handheld devices, or electric sharpeners, the key is to maintain the correct angle and use the appropriate grit for your blade. Leading manufacturers such as Shimomura Kogyo, Kyocera, King, Takeuchi, and Asahi Industry continue to uphold Japan's legacy of precision sharpening. Investing in the right sharpener and mastering sharpening techniques will ensure your Japanese knives perform at their best for years to come.

Japanese sharpeners can handle a variety of knives including stainless steel, high-carbon steel, titanium, and ceramic blades. However, some sharpeners, like the TOGISHI, are not suitable for ceramic knives.
Sharpening frequency depends on usage but generally every 1-2 months is recommended, with regular honing weekly to maintain the edge between sharpenings.
Yes, many Japanese knives can be sharpened at home using whetstones or handheld sharpeners. However, professional sharpening once a year is advisable for optimal blade care.
Honing realigns the blade's edge without removing metal, maintaining sharpness. Sharpening removes metal to restore a dull or damaged edge.
Some electric sharpeners are designed for Japanese knives with appropriate angle guides. However, they may remove more metal than manual methods and should be used carefully.